Hello everyone. I’m going to give you a brief introduction to the Juniper JNCIS-SP JN0-363 course that I created on Udemy. We’re just gonna have a quick look at what Juniper suggests that you need to know for the Juniper JNCIS-SP JN0-363 tests you on, and then we’ll have a little look and see whether that’s covered in the Udemy course.

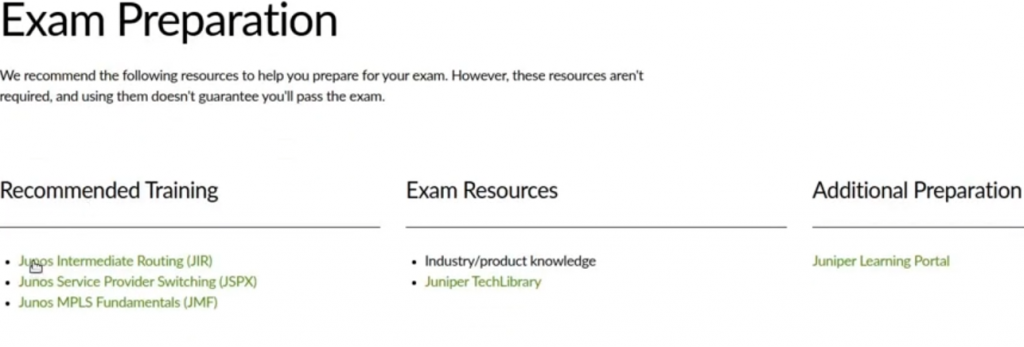
Okay. So. The recommended training is the Juniper JNCIS-SP JN0-363 Junos Intermediate Routing Routine, the Junos Service provider switching, and the Junos MPLS fundamentals. So let’s have a look at the exam objectives. Okay, so under the Protocol independent Routing , they want you to identify the concepts, operation or functionality.

Of various protocol, independent routing concepts. So this is non-dynamic rooting. So they want you to know static, aggregate, and generated routes and Martian addresses. Let’s have a look at my course and see what we’ve done here. So under the protocol Intermediate routing. Okay, so we have static routing qualified.
Next hop, which is like first is static route, static default options, aggregated routes and Martian routes. Okay, so it looks like we’ve covered them. Routing instances and rib groups. Load balancing and filter based forwarding. Let’s see if we cover. . So we have our Marshall dresses, our load balancing and our filter based forwarding.
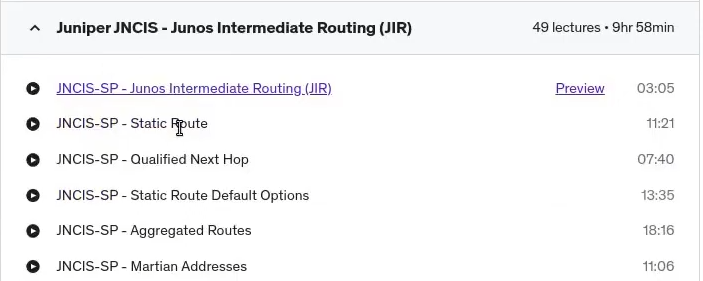

We also have routing instances and we have our rib groups. So it looks like we’ve covered everything for the protocol. Independent routing. Let’s have a look at the open, shortest path first. So they want you to know, , how to see the link state database, the OSPF packet types and the router id, adjacencies and neighbors designated and backup designated routers OSPF areas and router types, link state ad advertisements.

LSA packet types. So let’s have a little look and see what we have under OSPF. So we have. Basic theory one and basic theory two, two videos on basic OSPF configuration and some basic OSPF configuration commands. We have the OSPF metrics. We also have the area theory. We have multi area, and then we have our stub, total stub and not so stubby areas.


we’ve got timers, basic authentication and bidirectional forwarding detection. All of these are for OSPF, so it looks like that is well covered. Let’s have a look at the ISIS now. So they want you to identify concepts, operation and functionality of ISIS s. So Link State Database, the ISIS protocol data units.

Type length values, adjacencies and neighbors levels and areas and designated intermediate system or DIS and the metrics. Let’s have a little look and see what we have here. So we have a bit of ISIS theory, intra area configuration, a full area configuration with level one, level two routers. We have full mesh area.

On ISIS and we have authentication. And BFD on ISIS as well. Alright, let’s see what else they want you to know. So for bgp, they want you to know BGP basic operations, BGP message types, the attributes, the path selection, the internal and external iBGP and eBGP functions. Let’s see what we have here under bgp.

So we have basic bgp. . We have our first BGP config. We have our first route policy. We have eBGP to eBGP, route sharing, iBGP configs Next Hop Self. For iBGP, we have information on route reflectors. We have route selection theory and route preference. We have as path, and we have the BGP Med, so it looks like everything is covered for bgp.

Let’s have a look now under the Layer2, bridging or VLANs. So they want you to have a look at the service provider switching platforms, bridging elements and terminology, frame processing, virtual switch. QnQ tunneling. Okay, let’s have a look. Oh, let’s, I might have a look at the span tree while we’re here.

So, span tree, they want you to, , stp, rapid span tree, multiple span tree, the port rolls. , BPDU use spanning tree security. Okay, let’s have a look. See what we have under service provider. Switching.

Okay, so we have our bridge domains, our access and trunk ports into VLAN routing, rapid spanning tree vlan, spanning tree, and multiple spanning tree and spanning tree security. We have 802.1q, , versus 802.1ad. So QnQ we have, , the service provider switching key terms, framework Q and Q configurations, how to limit customer VLANs, Ctag normalization, VLAN rewrites, and then we have our multi chassis lag as well, and we have our standard lag also.


So it looks like we’ve covered everything , for SPAN tree, have look at MPLS. So we have MPLS, terminology, MPLS, packet, header, end-to-end packet flow forwarding labels and label information base, MPLS and routing tables. Rsvp, LDP. And this is new in this particular version of the exam segment routing.

So let’s have a little. What we have under our MPLS, so we have an MPLS overview, a brief overview on pseudo wires, how to enable MPLS, static label switch paths. An LDP Introduction. Introduction, how to set up ldp, RSVP basic configuration and introduction, bandwidth reservation, and. Rsvp. Explicit route objects are three parts, and we have an introduction to CSPF and the traffic engineering database.
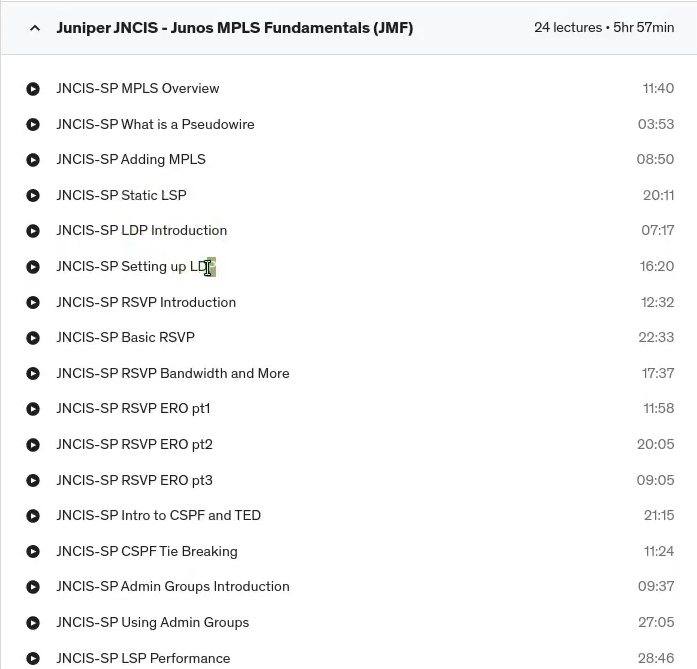
We’ve got, we go through the CSPF tie breaking rules. We have a look at admin groups and how to use admin groups. We have a look at how to configure LSP performance. We have a look at the primary and secondary LSP path and preemption. We also have a look at MPLS Fast Reroute and MPLS link protection, MPLS fake sharing, some miscellaneous features and some segment routing.

So it looks like we have that all covered. So then we have our IPV6. So IPV4 verse IPV6. The address types, address scope. Auto configuration. I SLAX and some tunneling. And under normal tunnels we have IP tunnels and gre. Okay. And under the high availability, we have link aggregation, which we’ve covered in the switching.

Graceful restart, graceful rooted engine switchover, non-stop bridging, nonstop rooting, bidirectional detection, which is covered in. All the routing routine protocols, VRRP, and in-service upgrade. So let’s have a look at our tunnels and services. So we have our IP tunnels and our GRE tunnels. How to do routing protocols over tunnels on Juniper devices.
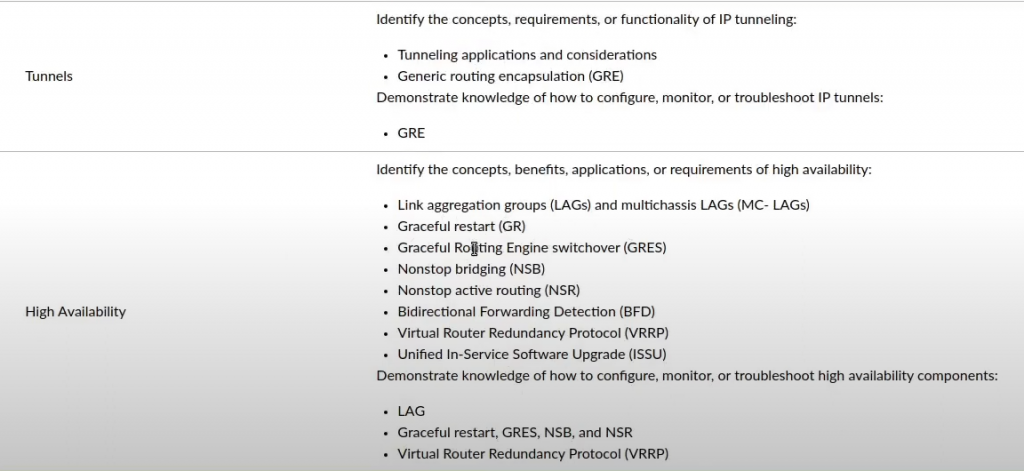
We have our VRRP. We have our in-service upgrade with GREs and non-stop routing. We have some IPV^ theory loop back configuration IPV6, static routes, how to do I OSPF, ISIS S, and BGP over IPV6 and how to do IPV6 over IPV4 tunnels. And I’ve also included here nearly two hours upskill for the JNCIS.
Enterprise. Predominantly because the JNCIS JN0-349 enterprise requires intermediate routing, which is included in the Juniper JNCIS-SP JN0-363. it’s the exact same course, and their switching course is very, very, very similar. So there only just needed to be a few videos for the upskill, basically because on service provider equipment, you are using MX series routers, whereas on the enterprise you are using ex series switches or QFX series if, , if you have to.
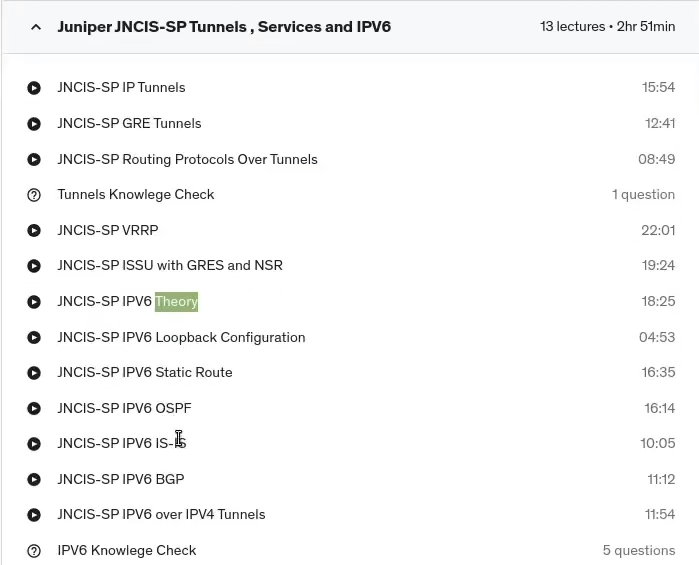
On the JNCIS JN0-349 enterprise section, we have, , how to do your VLANs access and trunk ports. RSTP , IRB interfaces, the voice vlan mac limiting DHCP snooping ARP Inspection and Source Guard storm control. and layer two firewall filters. So there will be a link below if, , you’re interested in partaking in this particular course.
If you are new to Juniper Networks they try my Juniper JNCIA JN0-104 Course that you can read about on this blog.